“旧日的幻影在高天内晃荡,降下不可磨灭的回忆。”
后缀数组
后缀数组并不属于 ,其靠两个特殊的数组用于维护有关后缀的内容,让其做到与 同样的功能。
后缀数组()由两个数组组成,其一为 ,其二为 。
其中 表示将所有后缀进行排序后排名为 的后缀,称为后缀数组,也称编号数组。
表示以 开头,即字符串 的排名,称为辅助数组,也叫排名数组。
满足性质:。
举一个例子
对于字符串 ,其后缀包括:
排序后得到:
对应得到:
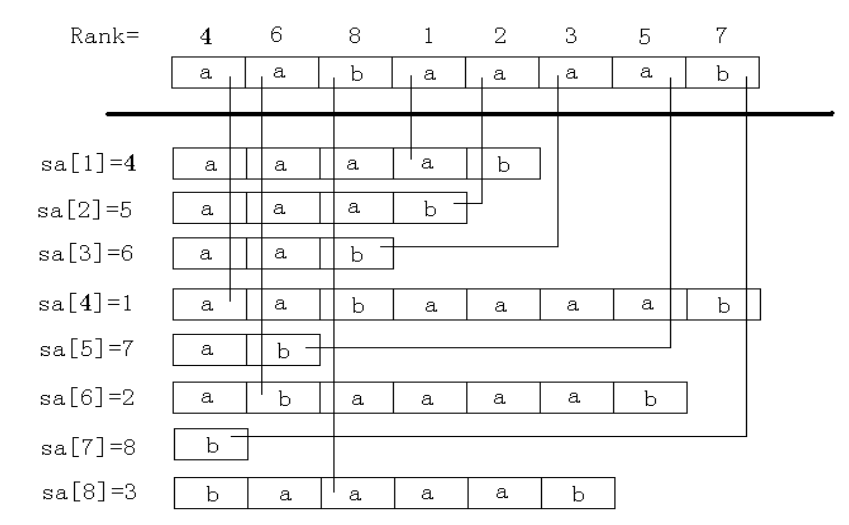
图片来自
暴力计算
我们将 个后缀进行存储,并补齐为同长字符串,然后直接进行 std::sort 得到 即可,时间复杂度 。
字符串哈希
考虑用更快捷的方式来表示每一个后缀,对于两个不同字符串的比较,一般情况下的比较是通过一位一位地枚举 ,直到找到一位满足 ,然后根据这一位进行判断,所以实际上, 之前的位数就是 的最长公共前缀。
所以我们使用字符串哈希进行存储,并二分查找字符串间的最长公共前缀进行排序,时间复杂度可以降至 。
题目简介
题目名称:后缀数组
题目来源:算法竞赛进阶指南
评测链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/142/
形式化题意:一个长度为 的字符串有 个后缀,其中 ,将 个后缀进行排序,用 表示排名为 的后缀,求 ,以及 。
数据范围:
AC Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
|
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define re register
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
template<class T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;
char ch=getchar(),t=0;
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') t|=ch=='-',ch=getchar();
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48),ch=getchar();
if(t) x=-x;
}
template<class T,class ...T1>
inline void read(T &x,T1 &...x1){ read(x),read(x1...); }
template<class T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9) write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
template<>
inline void write(bool x){ putchar(x?'1':'0'); }
template<>
inline void write(char c){ putchar(c); }
template<>
inline void write(char *s){ while(*s!='\0') putchar(*s++); }
template<>
inline void write(const char *s){ while(*s!='\0') putchar(*s++); }
template<class T,class ...T1>
inline void write(T x,T1 ...x1){ write(x),write(x1...); }
template<class T>
inline bool checkMax(T &x,T y){ return x<y?x=y,1:0; }
template<class T>
inline bool checkMin(T &x,T y){ return x>y?x=y,1:0; }
const int MAXN=5e5+10;
const int Base=131;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
char Str[MAXN];
ull Hash[MAXN],Pw[MAXN];
int Sa[MAXN],Len;
inline ull get(int l,int r)
{ return Hash[r]-Hash[l-1]*Pw[r-l+1]; }
inline int getLcp(int s1,int s2)
{
int l=0,r=std::min(Len-s1,Len-s2)+1,res=0;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(get(s1,s1+mid-1)==get(s2,s2+mid-1)) l=mid+1,res=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
return res;
}
inline bool cmp(int s1,int s2)
{
int len=getLcp(s1,s2);
int v1=s1+len>Len?-INF:Str[s1+len];
int v2=s2+len>Len?-INF:Str[s2+len];
return v1<v2;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s",Str+1),Pw[0]=1;
Len=std::strlen(Str+1);
for(int i=1;i<=Len;++i)
{
Pw[i]=Pw[i-1]*Base;
Hash[i]=Hash[i-1]*Base+Str[i];
Sa[i]=i;
}
std::sort(Sa+1,Sa+Len+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=Len;++i) write(Sa[i]-1,' ');
write("\n0 ");
for(int i=2;i<=Len;++i) write(getLcp(Sa[i-1],Sa[i]),' ');
return 0;
}
|
倍增
我们对 进行扩展,记录 限制长度为 的后缀数组。这样的话,我们可以很容易地得到 ,因为这样只需要把单个字母进行排序即可。
假设当前我们已经得到了 的值,接下来的一步是求 ,将 作为第一关键字和第二关键字进行排序,可以得到所有的 ,从而求出所有的 。
这样,当处理的 时,所得到的 就是我们需要的后缀数组了。
倍增中排序的合理性
对于两个同长度的字符串进行排序的时候,考虑划分,会出现以下两种情况:
- 两个字符串的前半部分不同,比较出大小;
- 两个字符串的前半部分相同,通过后半部分比较出大小。
所以可以用 作为第一关键字, 作为关键字,代表前半部分与后半部分的比较。
总时间复杂度 。
倍增与基数排序
考虑到瓶颈在排序的 上,所以考虑优化排序。我们学过的所有排序中,归并,桶排等都是 的,但基于后缀数组的特殊比较我们考虑用基数排序进行实现。
但是基数排序的常数十分大,甚至在特殊数据下不如快排(所以一般甚至可以直接写 std::stable_sort 会快一点),所以会有一系列的优化,但最后常数依然较大,但是至少可以限制在 范围内了。
给出一个常熟较小的模板。
参考实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| const int MAXN=1e6+10;
int N,M=127;
char Str[MAXN];
int Sa[MAXN],Rk[MAXN],Cnt[MAXN],Id[MAXN];
int Key[MAXN],Lstrk[MAXN];
inline bool cmp(int i,int j,int w)
{ return Lstrk[i]==Lstrk[j]&&Lstrk[i+w]==Lstrk[j+w]; }
int main()
{
scanf("%s",Str+1);
N=std::strlen(Str+1);
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i) ++Cnt[Rk[i]=Str[i]];
for(int i=1;i<=M;++i) Cnt[i]+=Cnt[i-1];
for(int i=N;i>=1;--i) Sa[Cnt[Rk[i]]--]=i;
for(int w=1,p,i;;w<<=1,M=p)
{
for(p=0,i=N;i>N-w;--i) Id[++p]=i;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i) if(Sa[i]>w) Id[++p]=Sa[i]-w;
std::memset(Cnt,0,sizeof(Cnt));
for(i=1;i<=N;++i) ++Cnt[Key[i]=Rk[Id[i]]];
for(i=1;i<=M;++i) Cnt[i]+=Cnt[i-1];
for(i=N;i>=1;--i) Sa[Cnt[Key[i]]--]=Id[i];
std::memcpy(Lstrk+1,Rk+1,N*sizeof(int));
for(p=0,i=1;i<=N;++i) Rk[Sa[i]]=cmp(Sa[i],Sa[i-1],w)?p:++p;
if(p==N)
{
for(i=1;i<=N;++i) Sa[Rk[i]]=i;
break;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i) write(Sa[i],' ');
return 0;
}
|
SA-IS
后缀数组一共有 个线性构造的算法,其一 因为常数过大代码复杂我非常懒所以不在本文中提及,我们直接上手 算法,也就是 ,诱导排序求后缀数组。
但是用的不多,一般字符串哈希和倍增可以解决 的后缀数组问题,所以等我需要用到之后再来补充这一部分。
例题
后缀数组的简单运用
题目简介
题目名称:
题目来源:
评测链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2852
形式化题意:给定一个长度为 的数组。求出现了至少 次的子串的最长长度。
数据范围:
出现 次,意味着我们需要找到 个后缀使其 最长,而根据 的性质,我们需要在 中一个长度为 的区间使得 最长,所以我们直接处理出 并对所有长度为 的区间求最小值的最大值即可。时间复杂度取决于前半段处理后缀数组的时间和后半段处理区间的时间,最优可达到 ,我使用的是 ,可以通过。
AC Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
|
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define re register
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
template<class T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;
char ch=getchar(),t=0;
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') t|=ch=='-',ch=getchar();
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48),ch=getchar();
if(t) x=-x;
}
template<class T,class ...T1>
inline void read(T &x,T1 &...x1){ read(x),read(x1...); }
template<class T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9) write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
template<>
inline void write(bool x){ putchar(x?'1':'0'); }
template<>
inline void write(char c){ putchar(c); }
template<>
inline void write(char *s){ while(*s!='\0') putchar(*s++); }
template<>
inline void write(const char *s){ while(*s!='\0') putchar(*s++); }
template<class T,class ...T1>
inline void write(T x,T1 ...x1){ write(x),write(x1...); }
template<class T>
inline bool checkMax(T &x,T y){ return x<y?x=y,1:0; }
template<class T>
inline bool checkMin(T &x,T y){ return x>y?x=y,1:0; }
const int MAXN=2e4+10;
const int Base=131;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int N,K,a[MAXN];
ull Hash[MAXN],Pw[MAXN];
int Sa[MAXN],Height[MAXN];
inline ull get(int l,int r)
{ return Hash[r]-Hash[l-1]*Pw[r-l+1]; }
inline int getLcp(int s1,int s2)
{
int l=0,r=std::min(N-s1+1,N-s2+1),res=0;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(get(s1,s1+mid-1)==get(s2,s2+mid-1)) l=mid+1,res=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
return res;
}
inline bool cmp(int s1,int s2)
{
int len=getLcp(s1,s2);
int v1=s1+len>N?-INF:a[s1+len];
int v2=s2+len>N?-INF:a[s2+len];
return v1<v2;
}
int St[MAXN][26];
inline void build()
{
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i) St[i][0]=Height[i];
for(int s=1;(1<<s)<N;++s)
for(int i=1;i+(1<<s)-1<=N;++i)
St[i][s]=std::min(St[i][s-1],St[i+(1<<(s-1))][s-1]);
}
inline int query(int l,int r)
{
int k=std::log2(r-l+1);
return std::min(St[l][k],St[r-(1<<k)+1][k]);
}
inline int ans()
{
int l=1,r=l+K-2,res=0;
while(r<=N)
{
int s=query(l,r);
checkMax(res,s);
++l,++r;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
read(N,K),Pw[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i) read(a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i)
{
Pw[i]=Pw[i-1]*Base;
Hash[i]=Hash[i-1]*Base+a[i];
Sa[i]=i;
}
std::sort(Sa+1,Sa+N+1,cmp);
for(int i=2;i<=N;++i) Height[i]=getLcp(Sa[i-1],Sa[i]);
build();
write(ans());
return 0;
}
|
后缀数组的简单运用 II
题目简介
题目名称:
题目来源:
评测链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8023
形式化题意:给定两个数组 长度分别为 ,每次从 或者 的第一个选取到新的数组 中并在原数组中删除该数,求 的最小字典序。
数据范围:
考虑一种贪心的思考,不考虑后效性的话,当前的 和 哪个小选哪个,如果一样就往后比较 ,直到不同为止。
容易发现这样的做法和后缀数组极其相似,我们将所有的 求出来后双指针扫一遍即可。注意要把 合并后再扫,且 之间需要一个 作分隔符。
字符串哈希的 过不了,但还是有 。
如果换成倍增的 的话就可以通过了,但是因为常数过大如果不开 只有 就太离谱。
